11.4. The Stedelijk Museum Amsterdam problem#
Python code for the Stedelijk Museum Amsterdam design problem (Chapter 9.3). Python code for the shopping mall design problem revisited non-linear example (Chapter 7.2).
Note
Press the rocket symbol on the top right of the page to make the page interactive and play with the code!
Note#
This notebook can be run directly in the online teachbook. If you prefer to execute the code in your own local environment, please refer to Appendix 11.6: (Chapter 11.6) for instructions and a download link to the ZIP folder containing all required example files.
Import Packages#
This script is fairly similar to the non-linear shopping mall example. Only the preference functions for objective 1 and 2 are changed, together with the weights.
Note that the non-linear preference curves are created by using an interpolation function called pchip_interpolation.
# ==== SAFE MATPLOTLIB BOOTSTRAP (run this cell first) ====
import os, sys, importlib
def _in_ipython_kernel():
try:
from IPython import get_ipython
ip = get_ipython()
return bool(ip) and hasattr(ip, "kernel")
except Exception:
return False
# Safely backed, before importing Pyplot
import matplotlib
_backend_set = False
if _in_ipython_kernel():
try:
importlib.import_module("matplotlib_inline.backend_inline")
matplotlib.use("module://matplotlib_inline.backend_inline", force=True)
_backend_set = True
except Exception as e:
print("[warn] inline backend niet beschikbaar/compatibel:", e)
if not _backend_set:
try:
matplotlib.use("Agg", force=True)
print("[info] Using Agg backend (no GUI).")
except Exception as e:
print("[warn] Agg backend kon niet gezet worden:", e)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Show plt.show(), for using agg.
try:
from IPython.display import display, Image
def _safe_show():
import uuid
fname = f"_plot_{uuid.uuid4().hex}.png"
plt.savefig(fname, bbox_inches="tight")
display(Image(filename=fname))
plt.close('all')
if matplotlib.get_backend().lower() == "agg":
plt.show = _safe_show
except Exception:
# No IPython: show will not work
pass
# Optionial, defaults
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams.update({
"figure.dpi": 100,
"savefig.dpi": 120,
"figure.figsize": (10, 5),
})
# Imports
import sys
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import pchip_interpolate
from genetic_algorithm_pfm import GeneticAlgorithm
Set Weights for Different Objectives#
Set weights for the different objectives.
# set weights for the different objectives
w1 = .5
w2 = 1/24
w3 = 1/24
w4 = 1/24
w5 = 1/24
w6 = 1/24
w7 = 1/24
w8 = 1/24
w9 = 1/24
w10 = 1/24
w11 = 1/24
w12 = 1/24
w13 = 1/24
def objective_p1(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to minimize the investment.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([70, 71, 74], [100, 70, 0], -((2580-2950) * 14142 + 2950 * (p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7) * 100 + 1400 * (s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 +s5) * 100))
def objective_p2(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p1.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([79.01, 97.03, 101.54], [0, 20, 100], p1)
def objective_p3(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p2.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([13.54, 13.75, 14.38], [0, 70, 100], p2)
def objective_p4(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize s1.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([6.93, 6.97, 7.14], [0, 80, 100], s1)
def objective_p5(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p3.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([9.41, 10.50, 13.78], [0, 70, 100], p3)
def objective_p6(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize s2.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([.56, .62, .84], [0, 80, 100], s2)
def objective_p7(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p4.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([5.25, 6.52, 7.21], [0, 35, 100], p4)
def objective_p8(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize s3.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([74.23, 79.30, 99.60], [0, 80, 100], s3)
def objective_p9(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p5.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([62.64, 64.17, 70.31], [0, 80, 100], p5)
def objective_p10(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize s4.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([12.07, 12.95, 16.48], [0, 80, 100], s4)
def objective_p11(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p6.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([31.67, 37.02, 39.90], [0, 35, 100], p6)
def objective_p12(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize p7.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([16.24, 17.76, 22.30], [0, 70, 100], p7)
def objective_p13(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5):
"""
Objective to maximize s5.
"""
return pchip_interpolate([1.68, 1.91, 2.81], [0, 80, 100], s5)
def objective(variables):
"""
Objective function that is fed to the GA. Calles the separate preference functions that are declared above.
:param variables: array with design variable values per member of the population. Can be split by using array
slicing
:return: 1D-array with aggregated preference scores for the members of the population.
"""
# extract 1D design variable arrays from full 'variables' array
p1 = variables[:, 0]
p2 = variables[:, 1]
s1 = variables[:, 2]
p3 = variables[:, 3]
s2 = variables[:, 4]
p4 = variables[:, 5]
s3 = variables[:, 6]
p5 = variables[:, 7]
s4 = variables[:, 8]
p6 = variables[:, 9]
p7 = variables[:, 1]
s5 = variables[:, 11]
# calculate the preference scores
p_1 = objective_p1(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_2 = objective_p2(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_3 = objective_p3(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_4 = objective_p4(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_5 = objective_p5(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_6 = objective_p6(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_7 = objective_p7(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_8 = objective_p8(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_9 = objective_p9(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_10 = objective_p10(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_11 = objective_p11(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_12 = objective_p12(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
p_13 = objective_p13(p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5)
# aggregate preference scores and return this to the GA
return [w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8, w9, w10, w11, w12, w13], [p_1, p_2, p_3, p_4, p_5, p_6, p_7, p_8, p_9, p_10, p_11, p_12, p_13]
Define Constraints and Bounds#
Before we can run the optimization, we finally need to define the constraints and bounds.
def constraint_1(variables):
"""Constraint that checks if the sum of the areas x1 and x2 is not lower than 3,000 m2.
:param variables: ndarray of n-by-m, with n the population size of the GA and m the number of variables.
:return: list with scores of the constraint
"""
p1 = variables[:, 0]
p2 = variables[:, 1]
s1 = variables[:, 2]
p3 = variables[:, 3]
s2 = variables[:, 4]
p4 = variables[:, 5]
s3 = variables[:, 6]
p5 = variables[:, 7]
s4 = variables[:, 8]
p6 = variables[:, 9]
p7 = variables[:, 1]
s5 = variables[:, 11]
return (p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7) * 100 - (14142 + 24007) # < 0
def constraint_2(variables):
"""Constraint that checks if the sum of the areas x1 and x2 is not lower than 3,000 m2.
:param variables: ndarray of n-by-m, with n the population size of the GA and m the number of variables.
:return: list with scores of the constraint
"""
p1 = variables[:, 0]
p2 = variables[:, 1]
s1 = variables[:, 2]
p3 = variables[:, 3]
s2 = variables[:, 4]
p4 = variables[:, 5]
s3 = variables[:, 6]
p5 = variables[:, 7]
s4 = variables[:, 8]
p6 = variables[:, 9]
p7 = variables[:, 1]
s5 = variables[:, 11]
return (s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5) * 100 - 13000 # < 0
def constraint_3(variables):
"""Constraint to ensure the existing building on the central location is completely used
:param variables: ndarray of n-by-m, with n the population size of the GA and m the number of variables.
:return: list with scores of the constraint
"""
p1 = variables[:, 0]
p2 = variables[:, 1]
s1 = variables[:, 2]
p3 = variables[:, 3]
s2 = variables[:, 4]
p4 = variables[:, 5]
s3 = variables[:, 6]
p5 = variables[:, 7]
s4 = variables[:, 8]
p6 = variables[:, 9]
p7 = variables[:, 1]
s5 = variables[:, 11]
return ((2580-2950) * 14142 + 2950 * (p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7) * 100 + 1400 * (s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 +s5) * 100) - 74 * 1000000 # < 0
# define list with constraints
cons = [['ineq', constraint_1], ['ineq', constraint_2], ['ineq', constraint_3]]
# set bounds for all variables
b1 = [79.01, 101.54] # p1
b2 = [13.54, 14.38] # p2
b3 = [6.93, 7.14] # s1
b4 = [9.41, 13.78] # p3
b5 = [.56, .84] # s2
b6 = [5.25, 7.21] # p4
b7 = [74.23, 99.60] # s3
b8 = [62.64, 70.31] # p5
b9 = [12.07, 16.48] # s4
b10 = [31.67, 39.90] # p6
b11 = [16.24, 22.30] # p7
b12 = [1.68, 2.81] # s5
bounds = [b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8, b9, b10, b11, b12]
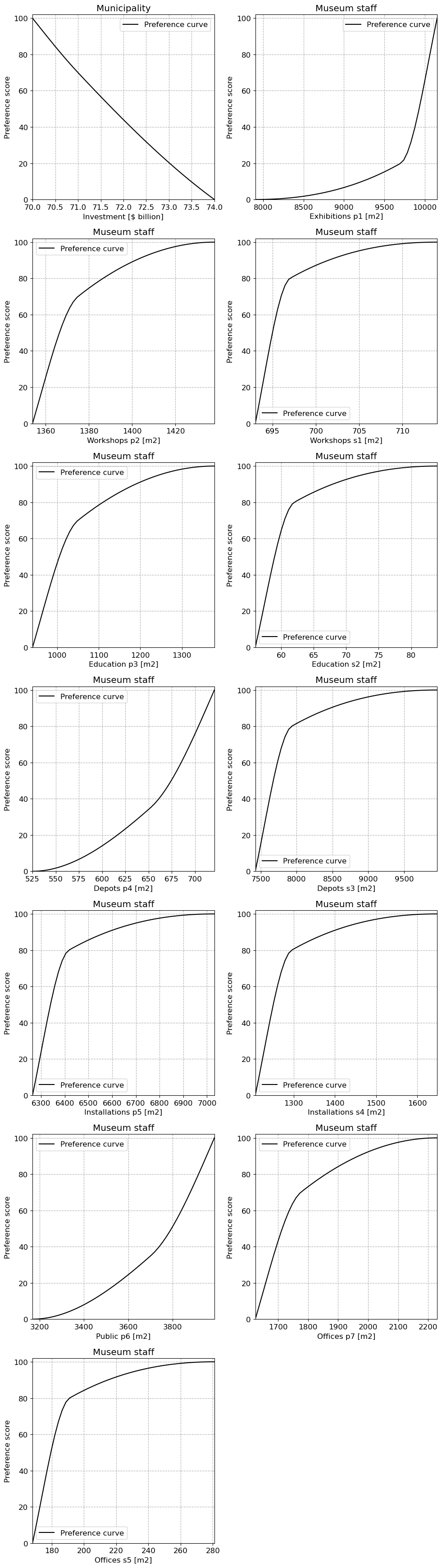
Graphical Output#
Setup the graphical output.
# create arrays for plotting continuous preference curves
c1 = np.linspace(70, 74)
c2 = np.linspace(7901, 10154)
c3 = np.linspace(1354, 1438)
c4 = np.linspace(693,714)
c5 = np.linspace(941, 1378)
c6 = np.linspace(56, 84)
c7 = np.linspace(525, 721)
c8 = np.linspace(7423,9960)
c9 = np.linspace(6264, 7031)
c10 = np.linspace(1207, 1648)
c11 = np.linspace(3167, 3990)
c12 = np.linspace(1624,2230)
c13 = np.linspace(168,281)
# calculate the preference functions
p1 = pchip_interpolate([70, 71, 74], [100, 70, 0], (c1))
p2 = pchip_interpolate([7901, 9703, 10154], [0, 20, 100], (c2))
p3 = pchip_interpolate([1354, 1375, 1438], [0, 70, 100], (c3))
p4 = pchip_interpolate([693, 697, 714], [0, 80, 100], (c4))
p5 = pchip_interpolate([941, 1050, 1378], [0, 70, 100], (c5))
p6 = pchip_interpolate([56, 62, 84], [0, 80, 100], (c6))
p7 = pchip_interpolate([525, 652, 721], [0, 35, 100], (c7))
p8 = pchip_interpolate([7423, 7930, 9960], [0, 80, 100], (c8))
p9 = pchip_interpolate([6264, 6417, 7031], [0, 80, 100], (c9))
p10 = pchip_interpolate([1207, 1295, 1648], [0, 80, 100], (c10))
p11 = pchip_interpolate([3167, 3702, 3990], [0, 35, 100], (c11))
p12 = pchip_interpolate([1624, 1776, 2230], [0, 70, 100], (c12))
p13 = pchip_interpolate([168, 191, 281], [0, 80, 100], (c13))
# create figure that plots all preference curves and the preference scores of the returned results of the GA
fig = plt.figure(figsize=((10,35)))
font1 = {'size':20}
font2 = {'size':15}
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = '12'
plt.rcParams['savefig.dpi'] = 300
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 1)
ax1.plot(c1, p1, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax1.set_xlim((70, 74))
ax1.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax1.set_title('Municipality')
ax1.set_xlabel('Investment [$ billion]')
ax1.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax1.grid()
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 2)
ax2.plot(c2, p2, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax2.set_xlim((7901, 10154))
ax2.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax2.set_title('Museum staff')
ax2.set_xlabel('Exhibitions p1 [m2]')
ax2.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax2.grid()
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 3)
ax3.plot(c3, p3, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax3.set_xlim((1354, 1438))
ax3.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax3.set_title('Museum staff')
ax3.set_xlabel('Workshops p2 [m2]')
ax3.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax3.grid()
ax3.legend()
ax3.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 4)
ax4.plot(c4, p4, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax4.set_xlim((693, 714))
ax4.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax4.set_title('Museum staff')
ax4.set_xlabel('Workshops s1 [m2]')
ax4.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax4.grid()
ax4.legend()
ax4.grid(linestyle = '--')
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 5)
ax5.plot(c5, p5, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax5.set_xlim((941, 1378))
ax5.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax5.set_title('Museum staff')
ax5.set_xlabel('Education p3 [m2]')
ax5.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax5.grid()
ax5.legend()
ax5.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 6)
ax6.plot(c6, p6, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax6.set_xlim((56, 84))
ax6.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax6.set_title('Museum staff')
ax6.set_xlabel('Education s2 [m2]')
ax6.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax6.grid()
ax6.legend()
ax6.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax7 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 7)
ax7.plot(c7, p7, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax7.set_xlim((525, 721))
ax7.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax7.set_title('Museum staff')
ax7.set_xlabel('Depots p4 [m2]')
ax7.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax7.grid()
ax7.legend()
ax7.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax8 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 8)
ax8.plot(c8, p8, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax8.set_xlim((7423, 9960))
ax8.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax8.set_title('Museum staff')
ax8.set_xlabel('Depots s3 [m2]')
ax8.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax8.grid()
ax8.legend()
ax8.grid(linestyle = '--')
ax9 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 9)
ax9.plot(c9, p9, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax9.set_xlim((6264, 7031))
ax9.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax9.set_title('Museum staff')
ax9.set_xlabel('Installations p5 [m2]')
ax9.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax9.grid()
ax9.legend()
ax9.grid(linestyle = '--')
ax10 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 10)
ax10.plot(c10, p10, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax10.set_xlim((1207, 1648))
ax10.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax10.set_title('Museum staff')
ax10.set_xlabel('Installations s4 [m2]')
ax10.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax10.grid()
ax10.legend()
ax10.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax11 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 11)
ax11.plot(c11, p11, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax11.set_xlim((3167, 3990))
ax11.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax11.set_title('Museum staff')
ax11.set_xlabel('Public p6 [m2]')
ax11.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax11.grid()
ax11.legend()
ax11.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax12 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 12)
ax12.plot(c12, p12, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax12.set_xlim((1624, 2230))
ax12.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax12.set_title('Museum staff')
ax12.set_xlabel('Offices p7 [m2]')
ax12.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax12.grid()
ax12.legend()
ax12.grid(linestyle = '--')
#fig = plt.figure()
ax13 = fig.add_subplot(7, 2, 13)
ax13.plot(c13, p13, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax13.set_xlim((168, 281))
ax13.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax13.set_title('Museum staff')
ax13.set_xlabel('Offices s5 [m2]')
ax13.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax13.grid()
ax13.legend()
ax13.grid(linestyle = '--')
ax1.legend()
ax2.legend()
ax3.legend()
ax4.legend()
ax5.legend()
ax6.legend()
ax7.legend()
ax8.legend()
ax9.legend()
ax10.legend()
ax11.legend()
ax12.legend()
ax13.legend()
fig.tight_layout()
#Two lines to make our compiler able to draw:
#fig.savefig("../engineeringdesign.education/static/smafunctions.png")
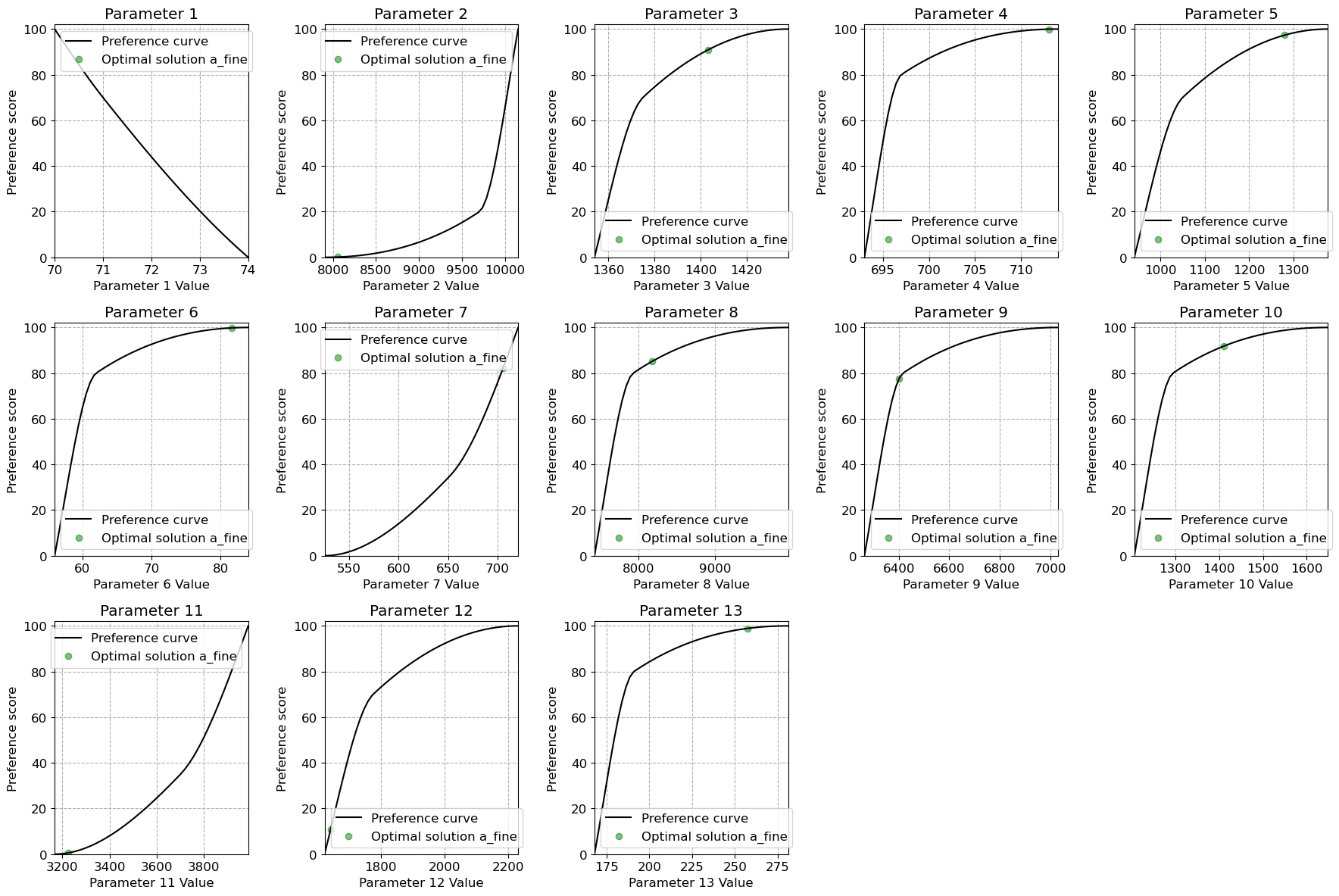
Optimization#
Now we have everything for the optimization, we can run it. For more information about the different options to configure the GA, see the docstring of GeneticAlgorithm (via help()) or chapter 4 of the reader.
Once we have the results, we can make some figures. First, the resulting design variables are plotted into the solution space. Secondly, we can plot the preference functions together with the results of the optimizations.
# We run the optimization with two paradigms
paradigm = ['minmax', 'a_fine']
marker = ['o', '*']
color = ['orange', 'green']
# Define the figure and axes before the loop
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(18, 12))
# Creating 13 subplots for the 13 preference scores
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 2)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 3)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 4)
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 5)
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 6)
ax7 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 7)
ax8 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 8)
ax9 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 9)
ax10 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 10)
ax11 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 11)
ax12 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 12)
ax13 = fig.add_subplot(3, 5, 13)
for i in range(1, 2):
# Make dictionary with parameter settings for the GA run with the IMAP solver
options = {
'n_bits': 24,
'n_iter': 400,
'n_pop': 500,
'r_cross': 0.8,
'max_stall': 16,
'aggregation': paradigm[i], # minmax or a_fine
'var_type': 'real'
}
# Run the GA and print its result
print(f'Run GA with IMAP')
ga = GeneticAlgorithm(objective=objective, constraints=cons, bounds=bounds, options=options)
score_IMAP, design_variables_IMAP, _ = ga.run()
p1, p2, s1, p3, s2, p4, s3, p5, s4, p6, p7, s5 = design_variables_IMAP
for n in range(12):
print(f'Optimal result for x{str(n+1)} = {round(design_variables_IMAP[n]*100)}')
investment = (2580 - 2950) * 14142 + 2950 * (p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7) * 100 + 1400 * (s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5) * 100
print('investment = ' + str(investment))
print('total primary location: ' + str((p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7) * 100))
print('total secondary location: ' + str((s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5) * 100))
"""
Now we have the results, we can make some figures. First, the resulting design variables are plotted into the solution
space. Secondly, we can plot the preference functions together with the results of the optimizations.
"""
# Calculate individual preference scores for the results of the GA to plot them on the preference curves
c1_res = (((2580 - 2950) * 14142 + 2950 * (p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7) * 100 + 1400 * (s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5) * 100) / 1000000)
p1_res = pchip_interpolate([70, 71, 74], [100, 70, 0], c1_res)
c2_res = design_variables_IMAP[0] * 100
p2_res = pchip_interpolate([7901, 9703, 10154], [0, 20, 100], c2_res)
c3_res = design_variables_IMAP[1] * 100
p3_res = pchip_interpolate([1354, 1375, 1438], [0, 70, 100], c3_res)
c4_res = design_variables_IMAP[2] * 100
p4_res = pchip_interpolate([693, 697, 714], [0, 80, 100], c4_res)
c5_res = design_variables_IMAP[3] * 100
p5_res = pchip_interpolate([941, 1050, 1378], [0, 70, 100], c5_res)
c6_res = design_variables_IMAP[4] * 100
p6_res = pchip_interpolate([56, 62, 84], [0, 80, 100], c6_res)
c7_res = design_variables_IMAP[5] * 100
p7_res = pchip_interpolate([525, 652, 721], [0, 35, 100], c7_res)
c8_res = design_variables_IMAP[6] * 100
p8_res = pchip_interpolate([7423, 7930, 9960], [0, 80, 100], c8_res)
c9_res = design_variables_IMAP[7] * 100
p9_res = pchip_interpolate([6264, 6417, 7031], [0, 80, 100], c9_res)
c10_res = design_variables_IMAP[8] * 100
p10_res = pchip_interpolate([1207, 1295, 1648], [0, 80, 100], c10_res)
c11_res = design_variables_IMAP[9] * 100
p11_res = pchip_interpolate([3167, 3702, 3990], [0, 35, 100], c11_res)
c12_res = design_variables_IMAP[10] * 100
p12_res = pchip_interpolate([1624, 1776, 2230], [0, 70, 100], c12_res)
c13_res = design_variables_IMAP[11] * 100
p13_res = pchip_interpolate([168, 191, 281], [0, 80, 100], c13_res)
# Plot the preference curves for the first iteration (i.e., i == 0) only
if i == 1:
# Create arrays for plotting continuous preference curves
c1 = np.linspace(70, 74)
c2 = np.linspace(7901, 10154)
c3 = np.linspace(1354, 1438)
c4 = np.linspace(693,714)
c5 = np.linspace(941, 1378)
c6 = np.linspace(56, 84)
c7 = np.linspace(525, 721)
c8 = np.linspace(7423,9960)
c9 = np.linspace(6264, 7031)
c10 = np.linspace(1207, 1648)
c11 = np.linspace(3167, 3990)
c12 = np.linspace(1624,2230)
c13 = np.linspace(168,281)
# Calculate the preference functions
p1 = pchip_interpolate([70, 71, 74], [100, 70, 0], c1)
p2 = pchip_interpolate([7901, 9703, 10154], [0, 20, 100], c2)
p3 = pchip_interpolate([1354, 1375, 1438], [0, 70, 100], c3)
p4 = pchip_interpolate([693, 697, 714], [0, 80, 100], c4)
p5 = pchip_interpolate([941, 1050, 1378], [0, 70, 100], c5)
p6 = pchip_interpolate([56, 62, 84], [0, 80, 100], c6)
p7 = pchip_interpolate([525, 652, 721], [0, 35, 100], c7)
p8 = pchip_interpolate([7423, 7930, 9960], [0, 80, 100], c8)
p9 = pchip_interpolate([6264, 6417, 7031], [0, 80, 100], c9)
p10 = pchip_interpolate([1207, 1295, 1648], [0, 80, 100], c10)
p11 = pchip_interpolate([3167, 3702, 3990], [0, 35, 100], c11)
p12 = pchip_interpolate([1624, 1776, 2230], [0, 70, 100], c12)
p13 = pchip_interpolate([168, 191, 281], [0, 80, 100], c13)
# Plot the preference curves
ax1.plot(c1, p1, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax1.set_xlim((70, 74))
ax1.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax1.set_title('Parameter 1')
ax1.set_xlabel('Parameter 1 Value')
ax1.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax1.grid(linestyle='--')
ax2.plot(c2, p2, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax2.set_xlim((7901, 10154))
ax2.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax2.set_title('Parameter 2')
ax2.set_xlabel('Parameter 2 Value')
ax2.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax2.grid(linestyle='--')
ax3.plot(c3, p3, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax3.set_xlim((1354, 1438))
ax3.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax3.set_title('Parameter 3')
ax3.set_xlabel('Parameter 3 Value')
ax3.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax3.grid(linestyle='--')
ax4.plot(c4, p4, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax4.set_xlim((693, 714))
ax4.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax4.set_title('Parameter 4')
ax4.set_xlabel('Parameter 4 Value')
ax4.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax4.grid(linestyle='--')
ax5.plot(c5, p5, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax5.set_xlim((941, 1378))
ax5.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax5.set_title('Parameter 5')
ax5.set_xlabel('Parameter 5 Value')
ax5.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax5.grid(linestyle='--')
ax6.plot(c6, p6, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax6.set_xlim((56, 84))
ax6.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax6.set_title('Parameter 6')
ax6.set_xlabel('Parameter 6 Value')
ax6.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax6.grid(linestyle='--')
ax7.plot(c7, p7, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax7.set_xlim((525, 721))
ax7.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax7.set_title('Parameter 7')
ax7.set_xlabel('Parameter 7 Value')
ax7.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax7.grid(linestyle='--')
ax8.plot(c8, p8, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax8.set_xlim((7423, 9960))
ax8.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax8.set_title('Parameter 8')
ax8.set_xlabel('Parameter 8 Value')
ax8.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax8.grid(linestyle='--')
ax9.plot(c9, p9, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax9.set_xlim((6264, 7031))
ax9.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax9.set_title('Parameter 9')
ax9.set_xlabel('Parameter 9 Value')
ax9.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax9.grid(linestyle='--')
ax10.plot(c10, p10, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax10.set_xlim((1207, 1648))
ax10.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax10.set_title('Parameter 10')
ax10.set_xlabel('Parameter 10 Value')
ax10.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax10.grid(linestyle='--')
ax11.plot(c11, p11, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax11.set_xlim((3167, 3990))
ax11.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax11.set_title('Parameter 11')
ax11.set_xlabel('Parameter 11 Value')
ax11.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax11.grid(linestyle='--')
ax12.plot(c12, p12, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax12.set_xlim((1624, 2230))
ax12.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax12.set_title('Parameter 12')
ax12.set_xlabel('Parameter 12 Value')
ax12.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax12.grid(linestyle='--')
ax13.plot(c13, p13, label='Preference curve', color='black')
ax13.set_xlim((168, 281))
ax13.set_ylim((0, 102))
ax13.set_title('Parameter 13')
ax13.set_xlabel('Parameter 13 Value')
ax13.set_ylabel('Preference score')
ax13.grid(linestyle='--')
# Scatter plot for the optimal solutions
ax1.scatter(c1_res, p1_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax2.scatter(c2_res, p2_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax3.scatter(c3_res, p3_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax4.scatter(c4_res, p4_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax5.scatter(c5_res, p5_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax6.scatter(c6_res, p6_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax7.scatter(c7_res, p7_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax8.scatter(c8_res, p8_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax9.scatter(c9_res, p9_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax10.scatter(c10_res, p10_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax11.scatter(c11_res, p11_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax12.scatter(c12_res, p12_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
ax13.scatter(c13_res, p13_res, label=f'Optimal solution {paradigm[i]}', color=color[i], alpha=0.5)
# Add legends and improve layout
ax1.legend()
ax2.legend()
ax3.legend()
ax4.legend()
ax5.legend()
ax6.legend()
ax7.legend()
ax8.legend()
ax9.legend()
ax10.legend()
ax11.legend()
ax12.legend()
ax13.legend()
# Adjust the layout
fig.tight_layout()
# Display the plot
plt.show()
Run GA with IMAP
The type of aggregation is set to a_fine
Generation Best score Mean Max stall Diversity Number of non-feasible results
No initial starting point for the optimization with the a-fine-aggregator is given. A random population is generated.
0 333333333.3333 333333333.3333 1 0.0 500
1 333333333.3333 333333333.3333 1 0.001 500
2 -100.0 333333333.3333 2 0.0 500
3 -100.0 333333333.3333 3 0.0 500
4 -100.0 333333333.3333 4 0.001 500
5 -100.0 333333333.3333 5 0.001 500
6 -100.0 333333333.3333 6 0.001 500
7 -100.0 333333333.3333 7 0.001 500
8 -100.0 333333333.3333 8 0.001 500
9 -100.0 333333333.3333 9 0.0 500
10 -100.0 333333333.3333 10 0.001 500
11 -100.0 333333333.3333 11 0.0 500
12 -100.0 333333333.3333 12 0.001 500
13 -100.0 333333333.3333 13 0.0 500
14 -100.0 333333333.3333 14 0.001 500
15 -100.0 333333333.3333 15 0.001 500
16 -100.0 333333333.3333 16 0.0 500
Stopped at gen 16
The number of generations is terribly close to the number of max stall iterations. This suggests a too fast convergence and wrong results.
Please be careful in using these results and assume they are wrong unless proven otherwise!
Execution time was 3.3313 seconds
Optimal result for x1 = 8056
Optimal result for x2 = 1403
Optimal result for x3 = 713
Optimal result for x4 = 1280
Optimal result for x5 = 82
Optimal result for x6 = 706
Optimal result for x7 = 8178
Optimal result for x8 = 6402
Optimal result for x9 = 1410
Optimal result for x10 = 3226
Optimal result for x11 = 1643
Optimal result for x12 = 257
investment = 76671597.74242996
total primary location: 22714.815222382542
total secondary location: 10639.594883143902