7. Optimization fundamentals#
Mathematical optimization is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. It can also be divided into constrained and unconstrained optimization or linear and non-linear optimization.
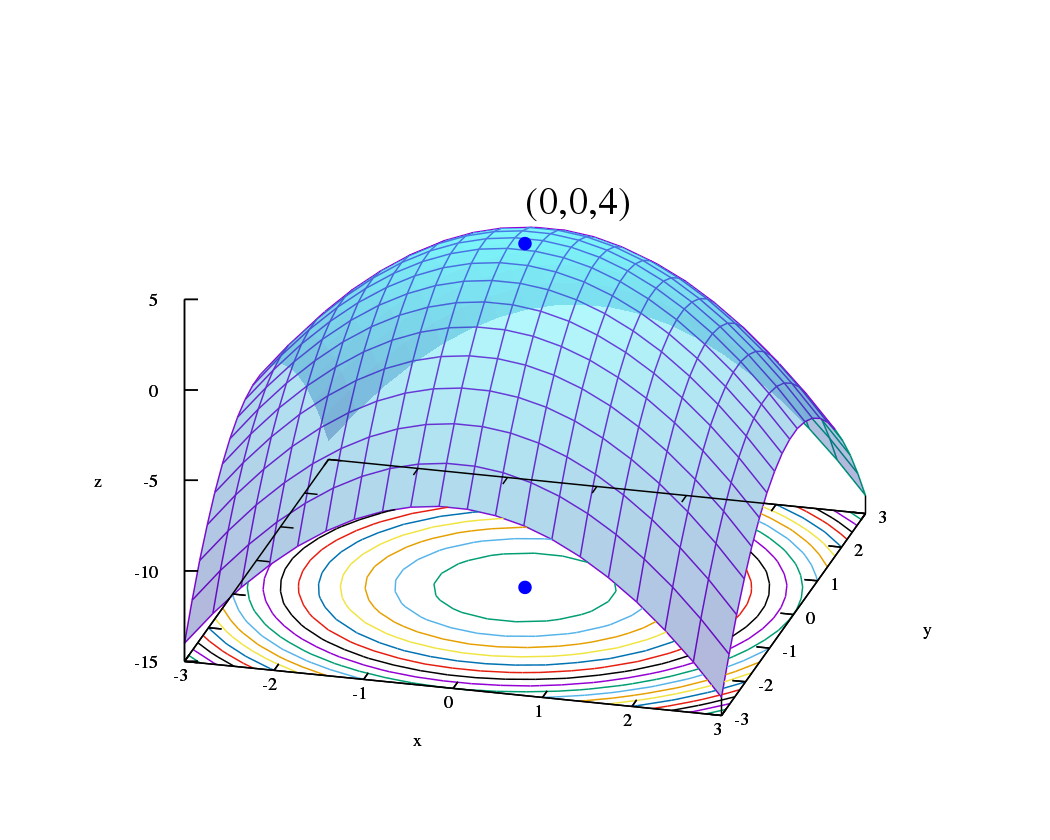
Graph of a surface given by z = f(x, y) = −(x² + y²) + 4. The global maximum at (x, y, z) = (0, 0, 4) is indicated by a blue dot.
