7.3. Products 1: floors#
Hollow core slabs#
Sections of hollow core slabs, prefabricated and prestressed
Applications: In all buildings hollow core slabs can be used as floors and roofs. Room for ducts and slots can be foreseen and provided during fabrication. Hollow core slabs are easily combined with hat-beams.
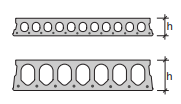
Fig. 7.4 Hollow core slabs#
Inverted U-slabs#
Inverted U-slabs with integrated isolation. The slabs are placed next to each other and the joints are filled with mortar.
Applications: Applicated as ground floor in residential and non residential buildings.
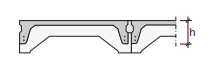
Fig. 7.5 Inverted U-slabs#
Combination floors#
Combination floors. Prefabricated inverted T-beams with EPS isolation and cast in situ concrete
Application: The type of floors is used frequently as ground floor above crawl spaces in residential building because of the simple construction and good isolation properties.
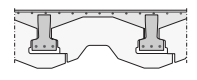
Fig. 7.6 Combination floors#
Composite steel-concrete floors#
A trapezoidal metal plate is used as working floor, formwork and reinforcement of the concrete compression layer.
Application: Used as floor system in (high rise) steel structures. Can be propped temporarily during casting which can lead to significant spans. The system offers relatively large flexibility for odd shaped floors.
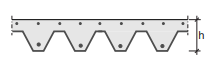
Fig. 7.7 Composite steel-concrete floors#
Composite plank floor#
A thin prefab concrete plate with protruding reinforcement is placed. In situ a compressive concrete layer is placed.
Applications: Floors of concrete structures in residential and non residential buildings.
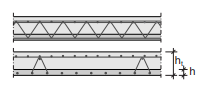
Fig. 7.8 Composite plank floor#
Double T-slabs#
Prefab, prestressed TT-beam.
Applications: prestressed, prefabricated floor beam system for large spans and/or heavily loaded beams. Is used mainly in non-residential buildings like parking garages and offices.
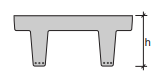
Fig. 7.9 Double T-slabs#