2.5. Variable loads 2: wind#
Loads caused by wind can be considerable and therefore have to be studied with care. For design purposes it is sometimes possible to use a simplified version of the code such as the one below.
Note
For a detailed analysis or for building with an irregular shape, always use NEN-EN 1991-1-4 General Actions - Wind Actions.
Determining the wind loading (simplified formula)#
\(F_i\) = Wind force on a structure or structural component [\(kN\)]
\(c_s * c_ d\) = Structural factor1 [-]
\(c_f\) = Force coefficient for structure or structural component [-]
\(q_p(z_e)\) = Peak velocity pressure at reference height2 ze [\(kN/m^2\)]
\(A_{ref}\) = Reference area on structure or structural component [\(m^2\)]
Note
The structural factor cscd can be taken as 1 for regular, low-rise buildings, for more information see NEN-EN 1991-1-4.
For high buildings (h>b) the velocity pressure may be assumed to decline towards ground level, for details see NEN-EN 1991-1-4.
Force coefficient for structures and strucural components: roofs and façades#
In this section the force coefficients for a simple building will be pointed out. As Eurocode is very extensive, the method for determining wind load will be pointed out using a simple structure. For more complicated shapes, use NEN-EN 1991-1-4. The directions of the different wind loads first need to be determined.
Note
Both these pressures need to be combined in the most unfavourable way.
The force coefficients corresponding to the different wind zones depend on the geometry of the building. For certain values the force coefficients are given. For other values linear interpolation is allowed. In this section only the force coefficients belonging to large surfaces are given (>10m2). For smaller surfaces see NEN-EN-1991-1-4.
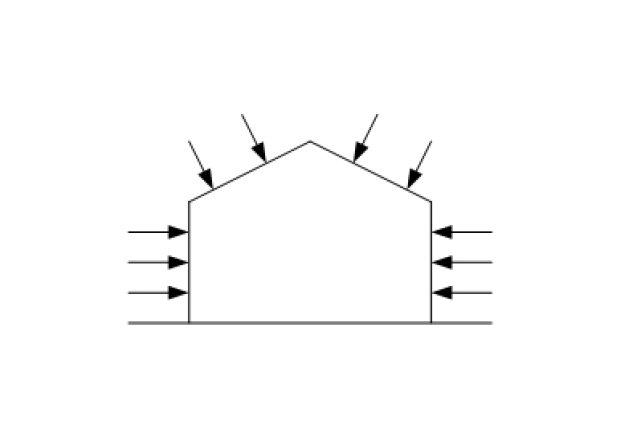
Fig. 2.4 Positive external pressure.#
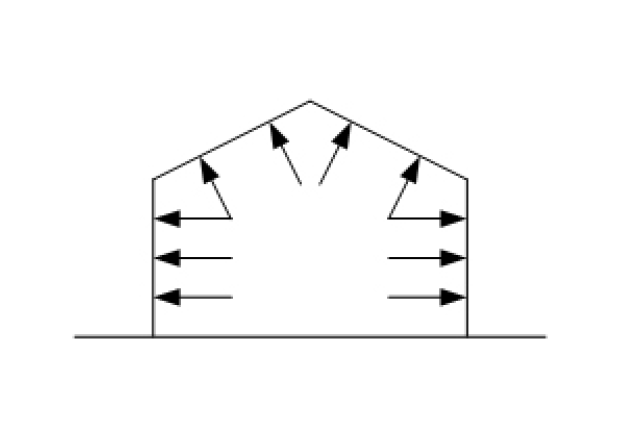
Fig. 2.5 Positive internal pressure.#
Building parameters#
\(h\) = highest point of building [\(m\)]
\(d\) = dimension in wind direction [\(m\)]
\(b\) = dimension in crosswind direction
\(e\) = \(b\) or \(2h\), whichever is smaller
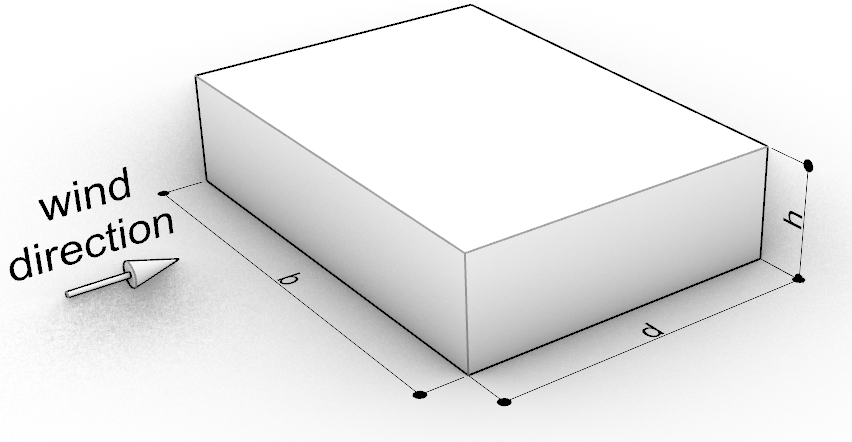
Fig. 2.6 Building parameters.#
Windzones for façades#
The different windzones on the façades of a building are shown below. Note that for different values of e and d the number of windzones on the side façades differ from 1 to 3. For buildings with duopitch roofs the same zones apply. The value h should then be taken as the height of the roof-ridge above ground level.
h/d |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
h/d = 5 |
-1.2 |
-0.8 |
-0.5 |
+0.8 |
-0.7 |
h/d = 1 |
-1.2 |
-0.8 |
-0.5 |
+0.8 |
-0.5 |
h/d ≤ 0.25 |
-1.2 |
-0.8 |
-0.5 |
+0.7 |
-0.3 |
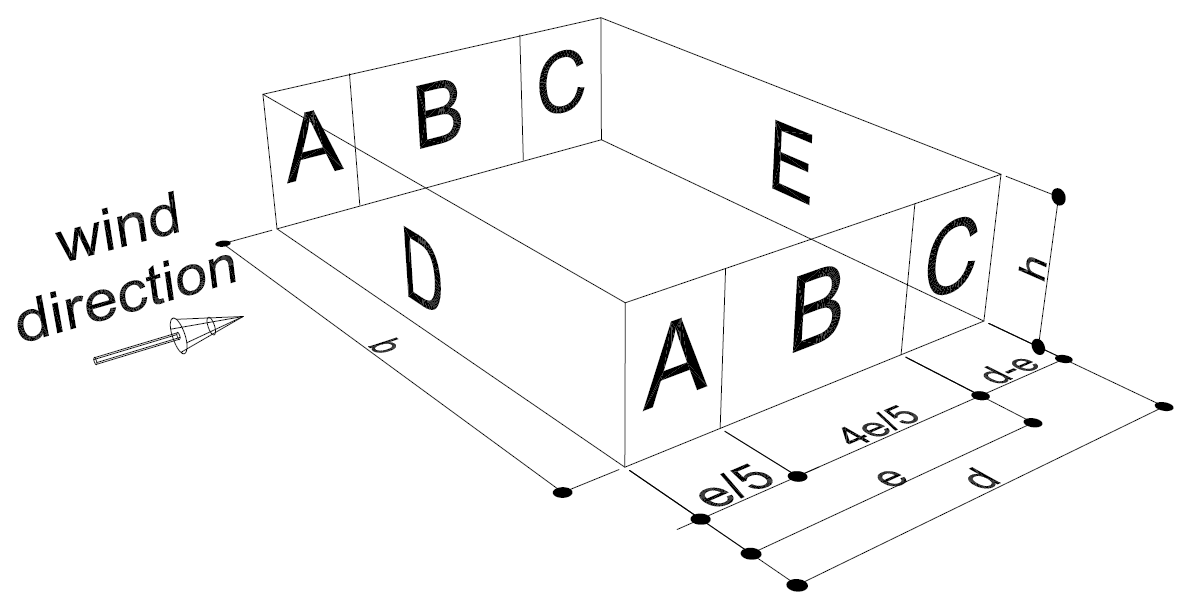
Fig. 2.7 Windzones for façades of a box-shaped building with e < d.#
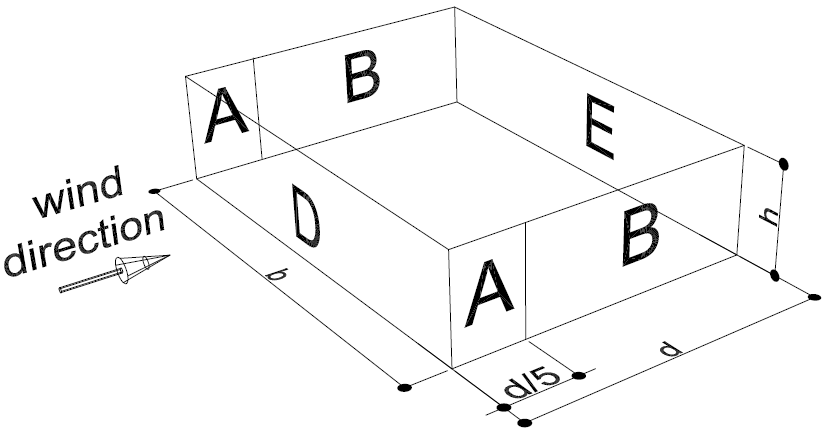
Fig. 2.8 Windzones for façades of a box-shaped building with e > d.#
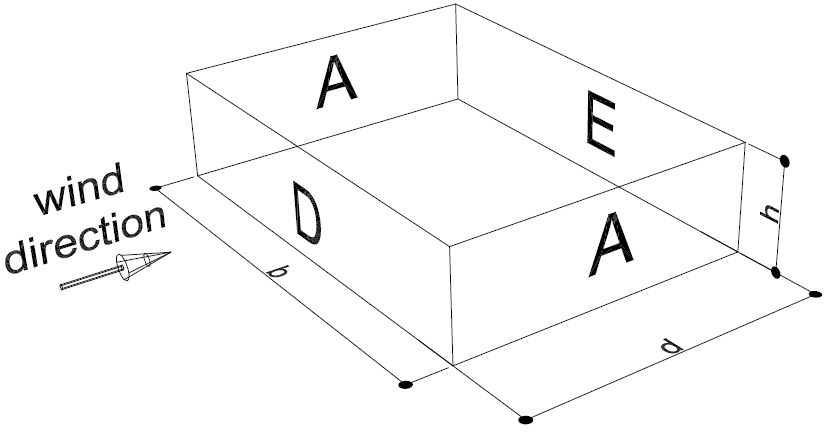
Fig. 2.9 Windzones for façades of a box-shaped building with e >= 5d.#
Windzones for flat roofs (closed buildings)#
Type |
F |
G |
H |
I |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Sharp eaves |
-1.8 |
-1.2 |
-0.7 |
+0.2/-0.2 |
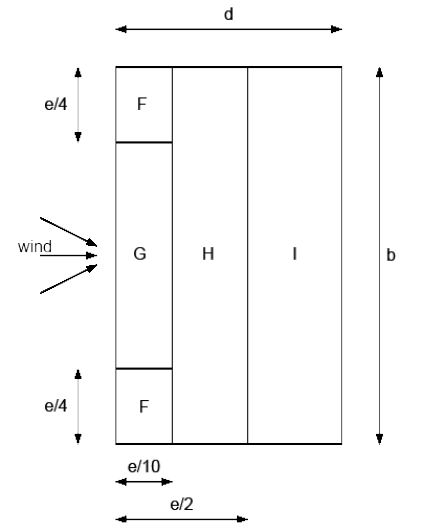
Fig. 2.10 Flat roofs, both wind directions (top view).#
Windzones for duopitch roofs#
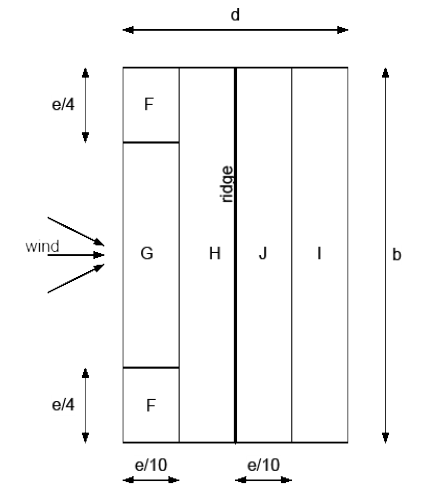
Fig. 2.11 Duopitch roofs, ridge crosswind (\(\theta = 0\)) (top view).#
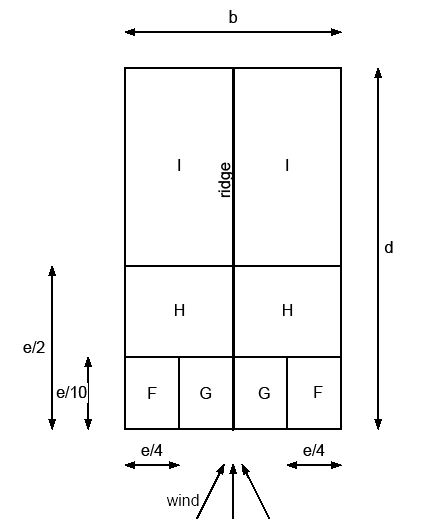
Fig. 2.12 Duopitch roofs, ridge parallel to wind (\(\theta = 90\)) (top view).#
Roof Angle (α) |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
5º |
-1.7 |
-1.2 |
-0.6 |
-0.6 |
+0.2 |
+0.0 |
+0.0 |
+0.0 |
-0.6 |
-0.6 |
|
15º |
-0.9 |
-0.8 |
-0.3 |
-0.4 |
-1.0 |
+0.2 |
+0.2 |
+0.2 |
+0.0 |
+0.0 |
|
30º |
-0.5 |
-0.5 |
-0.2 |
-0.4 |
-0.5 |
+0.7 |
+0.7 |
+0.4 |
+0.0 |
+0.0 |
|
45º |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
-0.2 |
-0.3 |
+0.7 |
+0.7 |
+0.6 |
+0.0 |
+0.0 |
|
60º |
+0.7 |
+0.7 |
+0.7 |
-0.2 |
-0.3 |
75º |
+0.8 |
+0.8 |
+0.8 |
-0.2 |
-0.3 |
Roof Angle (α) |
F |
G |
H |
I |
|---|---|---|---|---|
5º |
-1.6 |
-2.2 |
-0.7 |
-0.6 |
15º |
-1.3 |
-2.0 |
-0.6 |
-0.5 |
30º |
-1.1 |
-1.5 |
-0.8 |
-0.5 |
45º |
-1.1 |
-1.5 |
-0.9 |
-0.5 |
60º |
-1.1 |
-1.5 |
-0.8 |
-0.5 |
75º |
-1.1 |
-1.5 |
-0.8 |
-0.5 |
Windzones for canopies#
For canopies a resultant force can be determined (without the use of wind zones). This force represents the effect of all windzones on the total structure. The force acts on the points depicted below and is calculated with the same formula as other windloads. The location where this force acts depends on geometry and the sign of the overall force coefficient (\(c_f\)).
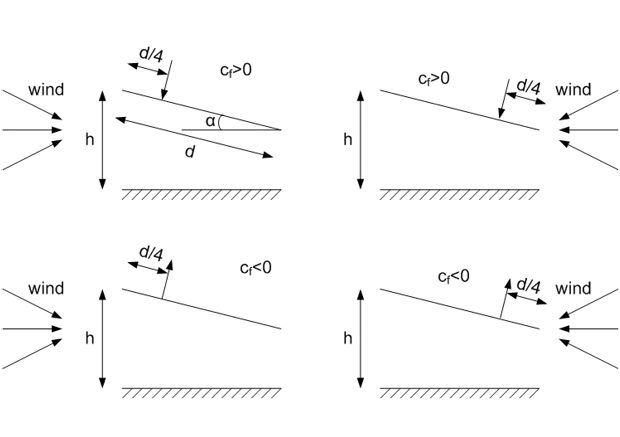
Fig. 2.13 Wind zones on canopies side view.#
Locally the wind pressure or suction on the canopy can of course be larger than the average. For the design of roofing elements and fixings these local loads must be taken into account. To calculate the local wind actions the canopy is divided in different windzones as shown below.
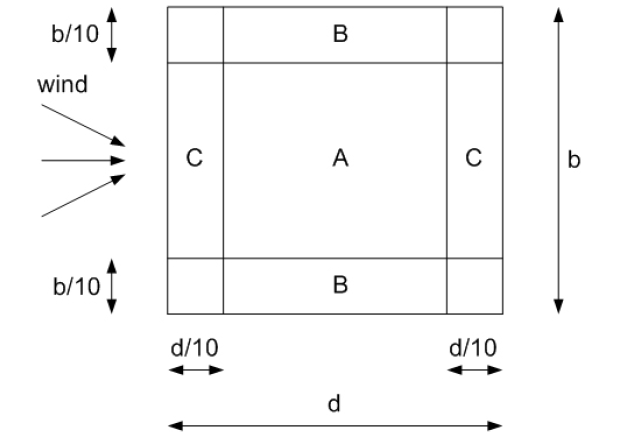
Fig. 2.14 Wind zones on canopies top view.#
Both the local and resultant force coefficient depents on the blockage (φ) under the canopy. The blockage is defined as the ratio of the area of the feasible, actual obstructions under the canopy divided by the cross sectional area under the canopy.
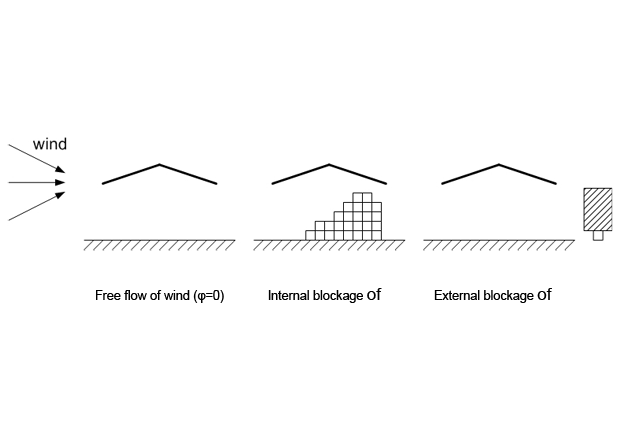
Fig. 2.15 Wind zones on canopies for different blockages under the canopy.#
Roof Angle (α) |
Blockage Factor (φ) |
Overall Force cf |
A |
B |
C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0º |
Maximum all φ |
+0.2 |
+0.5 |
+1.8 |
+1.1 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-0.5 |
-0.6 |
-1.3 |
-1.4 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
-1.3 |
-1.5 |
-1.8 |
-2.2 |
|
5º |
Maximum all φ |
+0.4 |
+0.8 |
+2.1 |
+1.3 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-0.7 |
-1.1 |
-1.7 |
-1.8 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
-1.4 |
-1.6 |
-2.2 |
-2.5 |
|
10º |
Maximum all φ |
+0.5 |
+1.2 |
+2.4 |
+1.6 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-0.9 |
-1.5 |
-2.0 |
-2.1 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
-1.4 |
-2.1 |
-2.6 |
-2.7 |
|
15º |
Maximum all φ |
+0.7 |
+1.4 |
+2.7 |
+1.8 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-1.1 |
-1.8 |
-2.4 |
-2.5 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
+1.4 |
-1.6 |
-2.9 |
-3.0 |
|
20º |
Maximum all φ |
+0.8 |
+1.7 |
+2.9 |
+2.1 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-1.3 |
-2.2 |
-2.8 |
-2.9 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
-1.4 |
-1.6 |
-2.9 |
-3.0 |
|
25º |
Maximum all φ |
+1.0 |
+2.0 |
+3.1 |
+2.3 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-1.6 |
-2.6 |
-3.2 |
-3.2 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
-1.4 |
-1.5 |
-2.5 |
-2.8 |
|
30º |
Maximum all φ |
+1.2 |
+2.2 |
+3.2 |
+2.4 |
Minimum φ=0 |
-1.8 |
-3.0 |
-3.8 |
-3.6 |
|
Minimum φ=1 |
-1.4 |
-1.5 |
-2.2 |
-2.7 |
1 For other edges lower force coefficients may be applicable, see NEN-EN-1991-1-4
2 For \(θ=0\), between \(α = 0º\) and \(45º\) the pressure changes rapidly between positive and negative values. For those roofs, four cases should be considered where the largest or smallest values of all areas F, G, and H are combined with the largest or smallest values in areas I and J. No mixing of positive and negative values is allowed on the same face.
Force coefficients for friction#
On faces parallel to the wind a friction force is acting. For design purposes it may be assumed that this force acts along all faces parallel to the wind direction. According NEN-EN-1991-1-4 this area can be reduced dependent on geometry.
Surface |
Friction Coefficient (\(c_{fr}\)) |
|---|---|
Smooth (e.g.: smooth concrete, steel) |
0.01 |
Rough (e.g.: rough concrete, tar-boards) |
0.02 |
Very rough (e.g.: ripples, folds, ribs) |
0.04 |
Force coefficients for internal pressure#
The force coefficients for internal pressure depend on the amount of openings in the façades and the geometry of the building. To avoid too complicated calculations, for design a note is stated in NEN-EN-1991-1-4: ‘Where it is not possible, or not considered justified, to estimate \(μ\) [dependend on geometry] then cpi should be taken as the more onerous (unfavourable red.) of +0,2 and -0,3.’ However, if the total amount of openings on two façades exeeds 30% of the area of those façades, the rules for canopies should be applied.
Windregions in the Netherlands#
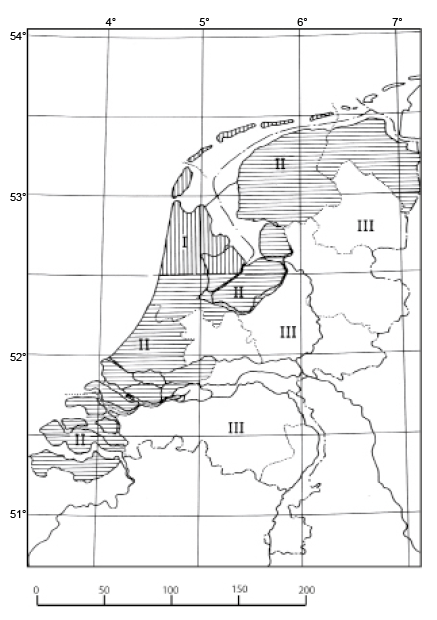
Fig. 2.16 Windregions in the Netherlands.#
Peak velocity pressure#
\(z_e\) [m] |
Coastal Area I |
Rural Area I |
Urban Area I |
Coastal Area II |
Rural Area II |
Urban Area II |
Coastal Area III |
Rural Area III |
Urban Area III |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
0.93 |
0.71 |
0.69 |
0.78 |
0.60 |
0.58 |
0.49 |
0.48 |
0.48 |
2 |
1.11 |
0.71 |
0.69 |
0.93 |
0.60 |
0.58 |
0.49 |
0.48 |
0.48 |
3 |
1.22 |
0.71 |
0.69 |
1.02 |
0.60 |
0.58 |
0.49 |
0.48 |
0.48 |
4 |
1.30 |
0.71 |
0.69 |
1.09 |
0.60 |
0.58 |
0.49 |
0.49 |
0.48 |
5 |
1.37 |
0.78 |
0.69 |
1.14 |
0.66 |
0.58 |
0.54 |
0.48 |
0.48 |
6 |
1.42 |
0.84 |
0.69 |
1.19 |
0.71 |
0.58 |
0.58 |
0.48 |
0.48 |
7 |
1.47 |
0.89 |
0.69 |
1.23 |
0.75 |
0.58 |
0.62 |
0.48 |
0.48 |
8 |
1.51 |
0.94 |
0.73 |
1.26 |
0.79 |
0.62 |
0.65 |
0.51 |
0.48 |
9 |
1.55 |
0.98 |
0.77 |
1.29 |
0.82 |
0.65 |
0.68 |
0.53 |
0.48 |
10 |
1.58 |
1.02 |
0.81 |
1.32 |
0.85 |
0.68 |
0.70 |
0.56 |
0.48 |
15 |
1.71 |
1.16 |
0.96 |
1.43 |
0.98 |
0.80 |
0.80 |
0.66 |
0.66 |
20 |
1.80 |
1.27 |
1.07 |
1.51 |
1.07 |
0.90 |
0.88 |
0.74 |
0.74 |
25 |
1.88 |
1.36 |
1.16 |
1.57 |
1.14 |
0.97 |
0.94 |
0.80 |
0.80 |
30 |
1.94 |
1.43 |
1.23 |
1.63 |
1.20 |
1.03 |
0.99 |
0.85 |
0.85 |
35 |
2.00 |
1.50 |
1.30 |
1.67 |
1.25 |
1.09 |
1.03 |
0.89 |
0.89 |
40 |
2.04 |
1.55 |
1.35 |
1.71 |
1.30 |
1.13 |
1.07 |
0.93 |
0.93 |
45 |
2.09 |
1.60 |
1.40 |
1.75 |
1.34 |
1.17 |
1.11 |
0.97 |
0.97 |
50 |
2.12 |
1.65 |
1.45 |
1.78 |
1.38 |
1.21 |
1.14 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
55 |
2.16 |
1.69 |
1.49 |
1.81 |
1.42 |
1.25 |
1.17 |
1.03 |
1.03 |
60 |
2.19 |
1.73 |
1.53 |
1.83 |
1.45 |
1.28 |
1.19 |
1.05 |
1.05 |
65 |
2.22 |
1.76 |
1.57 |
1.86 |
1.48 |
1.31 |
1.22 |
1.08 |
1.08 |
70 |
2.25 |
1.80 |
1.60 |
1.88 |
1.50 |
1.34 |
1.24 |
1.10 |
1.10 |
75 |
2.27 |
1.83 |
1.63 |
1.90 |
1.53 |
1.37 |
1.26 |
1.13 |
1.13 |
80 |
2.30 |
1.86 |
1.66 |
1.92 |
1.55 |
1.39 |
1.28 |
1.15 |
1.15 |
85 |
2.32 |
1.88 |
1.69 |
1.94 |
1.58 |
1.42 |
1.30 |
1.17 |
1.17 |
90 |
2.34 |
1.91 |
1.72 |
1.96 |
1.60 |
1.44 |
1.32 |
1.18 |
1.18 |
95 |
2.36 |
1.93 |
1.74 |
1.98 |
1.62 |
1.46 |
1.33 |
1.20 |
1.20 |
100 |
2.38 |
1.96 |
1.77 |
1.99 |
1.64 |
1.48 |
1.35 |
1.22 |
1.22 |
110 |
2.42 |
2.00 |
1.81 |
2.03 |
1.68 |
1.52 |
1.38 |
1.25 |
1.25 |
120 |
2.45 |
2.04 |
1.85 |
2.05 |
1.71 |
1.55 |
1.41 |
1.28 |
1.28 |
130 |
2.48 |
2.08 |
1.89 |
2.08 |
1.74 |
1.59 |
1.44 |
1.31 |
1.31 |
140 |
2.51 |
2.12 |
1.93 |
2.10 |
1.77 |
1.62 |
1.46 |
1.33 |
1.33 |
150 |
2.54 |
2.15 |
1.96 |
2.13 |
1.80 |
1.65 |
1.48 |
1.35 |
1.35 |
160 |
2.56 |
2.18 |
2.00 |
2.15 |
1.83 |
1.67 |
1.50 |
1.38 |
1.38 |
170 |
2.59 |
2.21 |
2.03 |
2.17 |
1.85 |
1.70 |
1.52 |
1.40 |
1.40 |
180 |
2.61 |
2.24 |
2.06 |
2.19 |
1.88 |
1.72 |
1.54 |
1.42 |
1.42 |
190 |
2.63 |
2.27 |
2.08 |
2.20 |
1.90 |
1.75 |
1.56 |
1.44 |
1.44 |
200 |
2.65 |
2.29 |
2.11 |
2.22 |
1.92 |
1.77 |
1.58 |
1.46 |
1.46 |