14.1. Effect vs Resistance#
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import norm
import statistics
Effect vs Resistance plotting function#
def plot_effect_vs_resistance(meanE, sdE, gamma_E, meanR, sdR, gamma_R):
# define lower and upper values of Effect E and Resistance R
Elower = 0.5*meanE
Eupper = 1.5*meanE
E = np.arange(Elower, Eupper, 1)
Rlower = 0.85*meanR
Rupper = 1.15*meanR
R = np.arange(Rlower, Rupper, 1)
# Plot x-axis range with 1 steps
x_axis = np.arange(-50, 450, 1)
# figure size in inches
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Calculating statistics
probE = (1 / (sdE * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp(-((0) ** 2) / (2 * sdE ** 2))
probErep = (1 / (sdE * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp((-(1.64 * sdE) ** 2) / (2 * sdE ** 2))
plt.text(Eupper, probE - 0.0015, "$\mu_E=$" + '{0:.0f}'.format(meanE), fontsize=10)
plt.text(Eupper, probE - 0.003, "$\sigma_E=$" + '{0:.2f}'.format(sdE), fontsize=10)
plt.text(Eupper, probE - 0.0045, "$\gamma_E=$" + '{0:.2f}'.format(gamma_E), fontsize=10)
Ed = (meanE + 1.64 * sdE) * gamma_E
probR = (1 / (sdR * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp(-((0) ** 2) / (2 * sdR ** 2))
probRrep = (1 / (sdR * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp((-(1.64 * sdR) ** 2) / (2 * sdR ** 2))
plt.text(Rupper, probR - 0.0015, "$\mu_R=$" + '{0:.0f}'.format(meanR), fontsize=10)
plt.text(Rupper, probR - 0.003, "$\sigma_R=$" + '{0:.2f}'.format(sdR), fontsize=10)
plt.text(Rupper, probR - 0.0045, "$\gamma_R=$" + '{0:.2f}'.format(gamma_R), fontsize=10)
Rd = (meanR - 1.64 * sdR) / gamma_R
# plot Ed values
plt.text(Rupper * 1.1, 0.5 * probR - 0.0075, "$E_d = E_{char}*\gamma_E=$" + '{0:.0f}'.format(Ed), fontsize=10)
plt.text(Rupper * 1.1, 0.5 * probR - 0.0090, "$R_d = R_{char}/\gamma_R=$" + '{0:.0f}'.format(Rd), fontsize=10)
plt.text(Rupper * 1.1, 0.5 * probR - 0.0105, "u.c. = $E_d / R_d = $" + '{0:.2f}'.format(Ed / Rd), fontsize=10)
# plot normal distribution curves for E (blue) and R (red)
plt.plot(x_axis, norm.pdf(x_axis, meanE, sdE), 'b')
plt.plot(x_axis, norm.pdf(x_axis, meanR, sdR), 'r')
plt.text(meanE + 5, probE, 'E', fontsize=15)
plt.text(meanE + 1.64 * sdE, probErep, "$E_{char}=$" + '{0:.0f}'.format(meanE + 1.64 * sdE), fontsize=10)
plt.text(meanE + 2.8 * sdE * gamma_E, probErep * 0.7, '$E_d$', fontsize=10)
# plot 5%-characteristic value with dashed red/blue lines
plt.plot([meanR - 1.64 * sdR, meanR - 1.64 * sdR], [0, probRrep], 'r--')
plt.plot([meanE + 1.64 * sdE, meanE + 1.64 * sdE], [0, probErep], 'b--')
# plot dimensioning value with drawn red/blue lines
plt.plot([(meanR - 1.64 * sdR) / gamma_R, (meanR - 1.64 * sdR) / gamma_R], [0, 0.7 * probErep], 'r-')
plt.plot([(meanE + 1.64 * sdE) * gamma_E, (meanE + 1.64 * sdE) * gamma_E], [0, 0.7 * probErep], 'b-')
plt.text(meanR + 5, probR, 'R', fontsize=15)
plt.text(meanR - 3.7 * sdR, probRrep, "$R_{char}=$" + '{0:.0f}'.format(meanR - 1.64 * sdR), fontsize=10)
plt.text(meanR - 4.5 * sdR / gamma_R, probErep * 0.7, '$R_{d}$', fontsize=10)
plt.xlabel("Effect (E, left) vs. Resistance (R, right) [unit could be e.g. load in kN or stress in MPa]")
plt.ylabel("Probability")
# plt.savefig("E_R_curves_highgamma_uc0.81_beta6_8.pdf", format="pdf", bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()
Reliability Z function#
def plot_Z(meanE, sdE, gamma_E, meanR, sdR, gamma_R):
# define lower and upper values of Effect E and Resistance R
Elower = 0.5*meanE
Eupper = 1.5*meanE
E = np.arange(Elower, Eupper, 1)
Rlower = 0.85*meanR
Rupper = 1.15*meanR
R = np.arange(Rlower, Rupper, 1)
# Plot x-axis range with 1 steps
x_axis = np.arange(-50, 450, 1)
# figure size in inches
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Calculating statistics
probE = (1 / (sdE * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp(-((0) ** 2) / (2 * sdE ** 2))
probErep = (1 / (sdE * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp((-(1.64 * sdE) ** 2) / (2 * sdE ** 2))
Ed = (meanE + 1.64 * sdE) * gamma_E
probR = (1 / (sdR * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp(-((0) ** 2) / (2 * sdR ** 2))
probRrep = (1 / (sdR * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))) * math.exp((-(1.64 * sdR) ** 2) / (2 * sdR ** 2))
Rd = (meanR - 1.64 * sdR) / gamma_R
# calculation reliability function
meanZ = meanR-meanE
sdZ=math.sqrt(sdE**2+sdR**2)
probZ=(1/(sdZ*math.sqrt(2*math.pi)))*math.exp(-((0)**2)/(2*sdZ**2))
beta=meanZ/sdZ
# plot Ed values
plt.text(Rupper * 1.1, 0.5 * probR - 0.0105, "u.c. = $E_d / R_d = $" + '{0:.2f}'.format(Ed / Rd), fontsize=10)
# plot normal distribution curves for E (blue) and R (red)
plt.plot(x_axis, norm.pdf(x_axis, meanE, sdE), 'b')
plt.plot(x_axis, norm.pdf(x_axis, meanR, sdR), 'r')
plt.plot(x_axis, norm.pdf(x_axis, meanZ, sdZ), 'g')
# plot averages with dash-dotted red/blue lines
plt.plot([meanR, meanR], [0, probR], 'r-.')
plt.plot([meanE, meanE], [0, probE], 'b-.')
plt.plot([meanZ,meanZ],[0,probZ], 'g-.')
plt.text(meanE + 5, probE, 'E', fontsize=15)
plt.text(meanR + 5, probR, 'R', fontsize=15)
plt.text(meanZ-10, probZ+0.001, 'Z=R-E', fontsize=15)
# arrows for beta
plt.plot([0,0],[0,probZ], 'k-.')
plt.plot([0,meanZ],[0.75*probZ,0.75*probZ], 'k-')
plt.plot([0,15],[0.75*probZ,0.80*probZ], 'k-')
plt.plot([0,15],[0.75*probZ,0.70*probZ], 'k-')
plt.plot([meanZ,meanZ-15],[0.75*probZ,0.80*probZ], 'k-')
plt.plot([meanZ,meanZ-15],[0.75*probZ,0.70*probZ], 'k-')
plt.text(meanZ/2, 0.8*probZ, "$\\mu_Z = \\beta \\cdot \\sigma_Z $", fontsize=10)
plt.text(meanR*1.25, 0.8*probZ, "$\\mu_Z = \\mu_R - \mu_E $", fontsize=10)
plt.text(meanR*1.25, 0.60*probZ, "$\\sigma_Z = \sqrt{\sigma_R^2 + \sigma_E^2} $", fontsize=10)
plt.text(meanR*1.25, 0.40*probZ, "$\\beta = \\mu_Z / \\sigma_Z = $"+'{0:.1f}'.format(beta), fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel("Effect (E, left) vs. Resistance (R, right) [unit could be e.g. load in kN or stress in MPa]")
plt.ylabel("Probability")
# plt.savefig("E_R_curves_highgamma_uc0.81_beta6.8.pdf", format="pdf", bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()
Initializing examples with data#
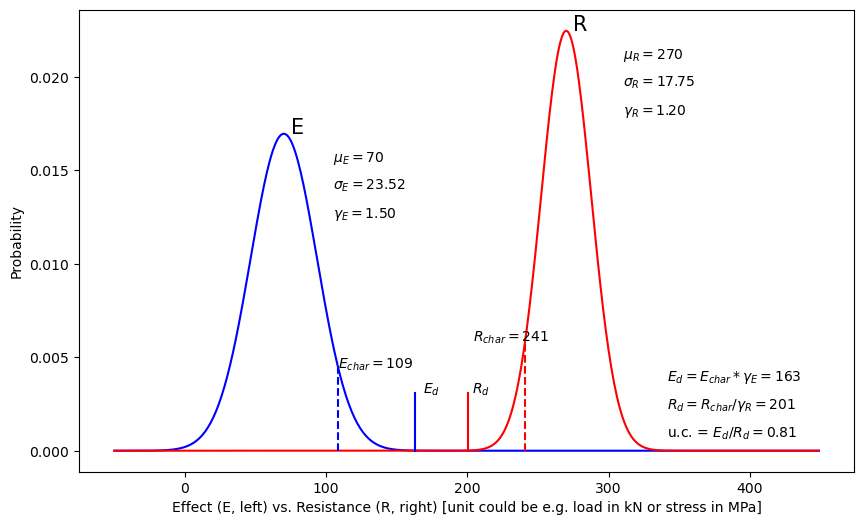
Using the functions defined above, plots can be generated. To do so, we need numerical input values. The numerical values for the example plot above are defined below and the functions executed.
meanE = 70
sdE = 23.52
gamma_E = 1.5
meanR = 270
sdR = 17.75
gamma_R = 1.2
plot_effect_vs_resistance(meanE, sdE, gamma_E, meanR, sdR, gamma_R)
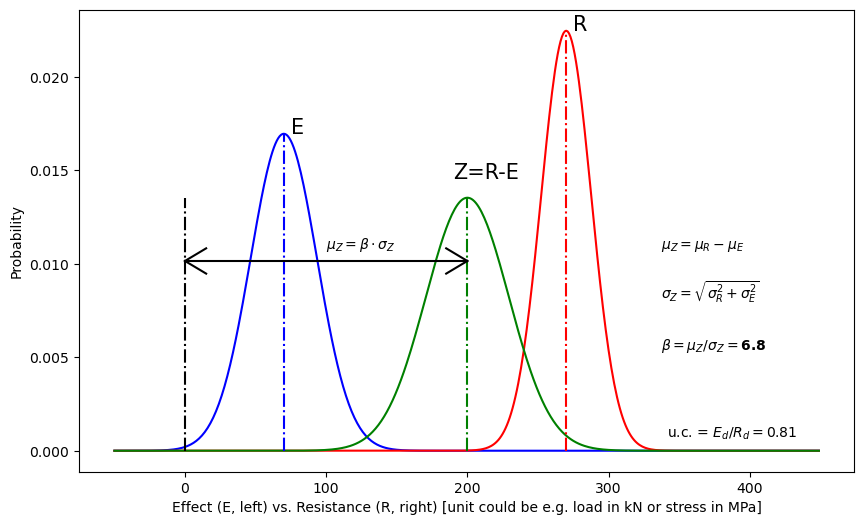
plot_Z(meanE, sdE, gamma_E, meanR, sdR, gamma_R)
Exercise
If \(\mu_E = 100\), \(\sigma_E = 20\), \(\mu_R = 240\) and \(\sigma_R = 20\), what are \(\mu_Z\), \(\sigma_Z\) and \(\beta\)? Use \(\gamma_E = 1.5\) and \(\gamma_R = 1.2\).
You might want to download some code cells or the full .ipynb page and put code in there to perform the calculations, and plot the graphs.
Solution
\(\mu_Z = \mu_R - \mu_E = 140\)
\(\sigma_Z = \sqrt{\sigma_R^2 + \sigma_E^2} = 22.4\)
\(\beta = \frac{\mu_Z}{\sigma_Z} = 6.3\)