7.1. Material characteristics#
This paragraph contains tables containing the different material properties of the defined concrete introduction strength classes [1].
Strenght and stiffness#
Material Property |
C12/15 |
C20/25 |
C30/37 |
C35/45 |
C45/55 |
C50/60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Density \(ρ_{rep}\) (kg/m³) |
2500 |
2500 |
2500 |
2500 |
2500 |
2500 |
Modulus of Elasticity (uncracked) \(E_{cm}\) (N/mm²) |
27000 |
30000 |
33000 |
34000 |
36000 |
37000 |
Mean Compressive Strength \(f_{cm}\) (N/mm²) |
20 |
28 |
38 |
43 |
53 |
58 |
Characteristic Cylinder Strength \(f_{ck}\) (N/mm²) |
12 |
20 |
30 |
35 |
45 |
50 |
Characteristic Cube Strength \(f_{ck;cube}\) (N/mm²) |
15 |
25 |
37 |
45 |
55 |
60 |
Mean Value Tensile Strength \(f_{ctm}\) (N/mm²) |
1.6 |
2.2 |
2.9 |
3.2 |
3.8 |
4.1 |
Characteristic Tensile Strength \(f_{ctk;0,05}\) (N/mm²) |
1.1 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.2 |
2.7 |
2.9 |
Strength#
Design compressive strength: \( \frac{f_{ck}}{\gamma} = \frac{f_{ck}}{1.5} \)
Design shear strength: \( b \cdot d \cdot 0.035 \cdot k^{\frac{3}{2}} \cdot \sqrt{f_{ck}} \) (lower bound, for exact value, see EC2). Shear resistance can be increased using shear reinforcement.
\( k = 1 + \sqrt{\frac{200}{d}} \leq 2 \); d in mm
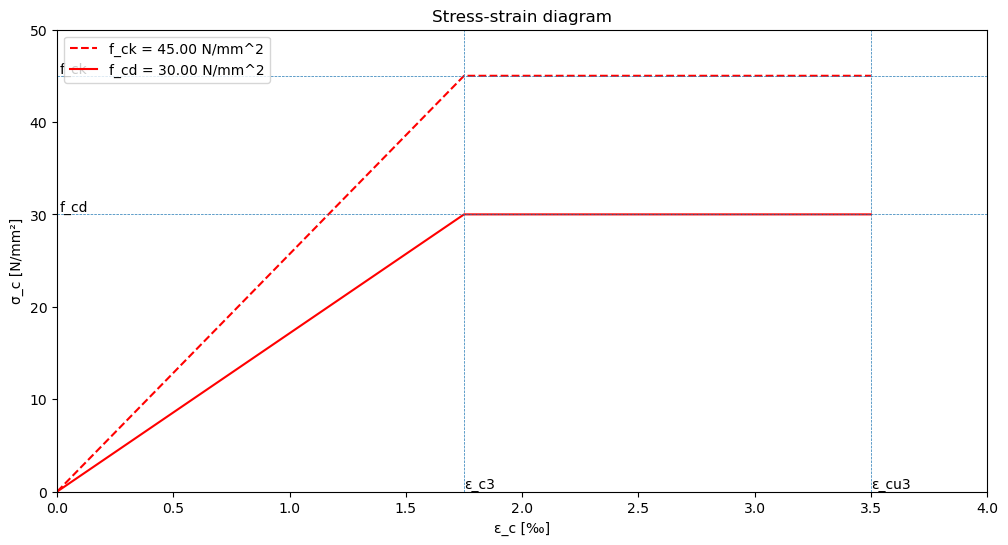
Stress-strain diagram#
\(σ_{c}\) : concrete compressive stress
\(ε_c\) : concrete compressive strain
\(f_{cd}\) : design compressive strength
\(ε_{c3}\) : strain at the start of plastic deformation
\(ε’_{bu}\) : limit strain
\(ε_{c3}\) : 1,75 ‰
\(ε_{cu3}\) : 3,50 ‰
Note
This diagram changes when higher strength classes are chosen. For the strength classes shown in the table in this paragraph these values are valid.